Gum Care
Gum disease or periodontal disease is an inflammatory condition of tissues surrounding the tooth, which can lead to a tooth loss. When the gum disease sets in, the toxins produced by the bacteria damage the teeth’s connective tissue and bone, effectively destroying them and fostering tooth loss. Our gum specialists can help detect any early signs of gum disease and problems in the hard-to-see gum areas. They can treat, control and prevent gum infections and help protect and preserve your teeth, which will contribute toward your overall good health.
Gum Inflammations & Infections
Gum inflammations and infections are a result of bacteria penetrating deep below the gum surface. If bacteria are permitted to increase for long periods of time, plaque is formed fostering more bacterial growth. They irritate the gums making them tender, inflamed and likely to bleed. As a gum infection progresses, the bone tends to recede. In some cases, the root of the tooth becomes exposed, occasionally causing tooth sensitivity. In advanced cases, pus may be produced causing pockets between the gum and tooth. Since bone recession is not visible, it is often left undetected by the naked eye.
Therefore, It is important to visit the dentist for professional examinations and dental cleanings to identify gum disease.
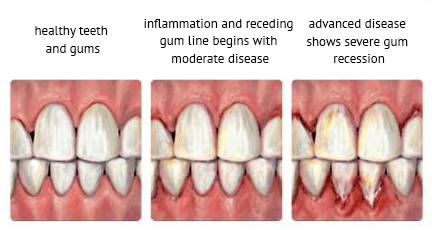
Types of Gum Disease
| Gingivitis | An inflammation of the gums, which is the initial stage of gum disease and the easiest stage to treat. The cause of gingivitis is plaque-the soft, sticky, colorless film or bacteria that forms constantly on the teeth and gums. |
| Periodontitis | A serious gum infection that destroys the soft tissue and bone that support your teeth. Periodontitis can cause tooth loss or worse, an increased risk of heart attack or stroke and other serious health problems. |
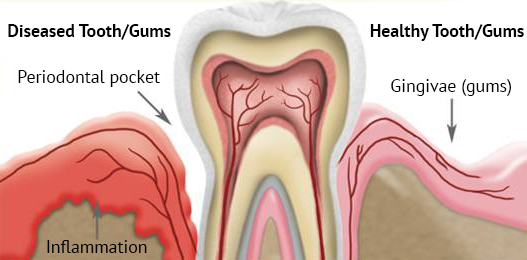
Common Signs of Gum Disease
- Bleeding gums during tooth brushing or flossing
- Gums are turning from pink to red
- Swollen, sensitive gums
- Gums have pulled away from the teeth
- Teeth are loose or changing position
- Any change in the bite
- Any change in the fit of partial dentures
- Constant bad breath or taste
Major Causes Of Gum Disease
- Poor Oral Hygiene Habits: Not following usual oral hygiene can cause gingivitis to develop.
- Hormone Changes: Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy, puberty and menopause may affect the organic balance in the mouth, and make teeth more susceptible to gum disease.
- Smoking / Tobacco Use: Smoking can lead to gum disease by causing tartar to build up in the teeth, destruction of gum tissue and bone loss. Smoking also causes the immune system to not work as well against fighting the infections of gum disease.
5 Steps to Prevention:
- Brush your teeth 2 times daily
- Floss your teeth 1 time daily
- Visit your dentist 2 times yearly
- Avoid smoking and smokeless tobacco
- Eat a balanced diet containing vitamin C, A and E